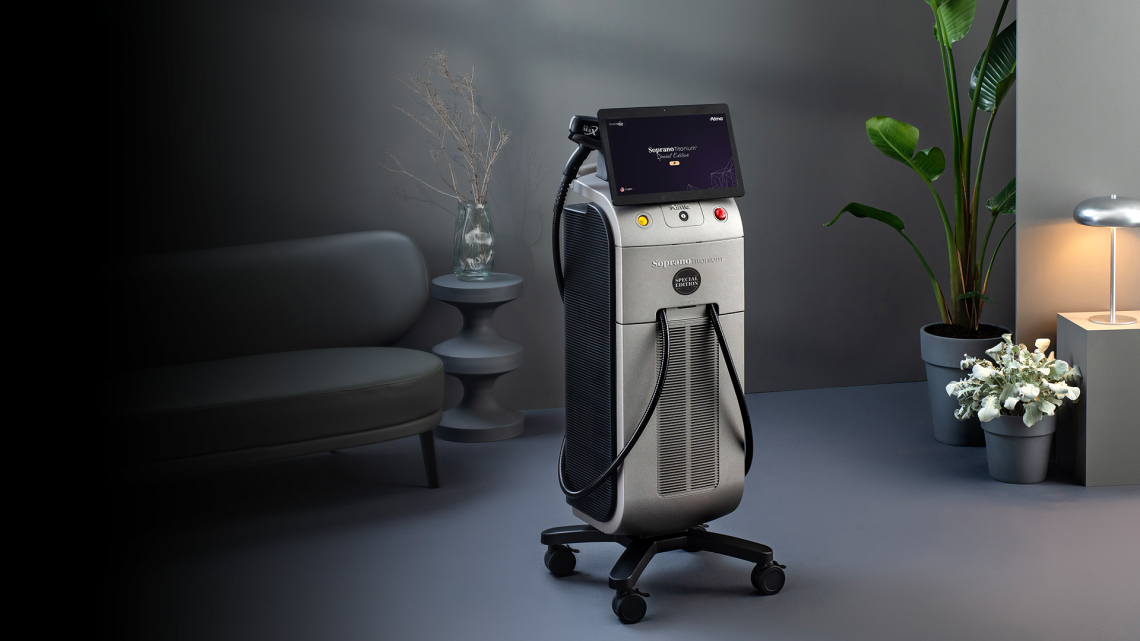
Introduction to the Titanium Laser Device In the ever-evolving world of technology, titanium laser devices stand out as some of the most advanced and versatile tools available. These devices, which harness the power of lasers combined with the exceptional properties of titanium, are transforming industries ranging from medical applications to manufacturing. This article delves into the characteristics, benefits, and wide-reaching uses of titanium laser devices.
What Is a Titanium Laser Device?
A titanium laser device is a laser technology that utilizes titanium, or titanium alloys, in its construction, either as the material for the laser’s housing or as part of its internal mechanisms. Titanium is known for its strength, lightweight nature, and high resistance to corrosion, which makes it ideal for use in laser devices that require durability, efficiency, and precision.
In most laser devices, lasers are used to focus light into a beam that can be employed for cutting, engraving, marking, or medical procedures. When paired with titanium, the laser’s power is enhanced because of the material’s unique properties. The high melting point, resilience, and biocompatibility of titanium also contribute to the laser device’s performance and longevity.
Key Features of Titanium Laser Devices
- Lightweight and Durable: Titanium is one of the strongest lightweight metals, offering high durability without adding unnecessary weight. This feature is crucial for industries like aerospace or precision manufacturing, where the combination of strength and lightweight materials is essential.
- Corrosion Resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, even in harsh environments such as saltwater or industrial settings. This resistance makes titanium laser devices ideal for medical applications, as well as outdoor or maritime uses, where the equipment is exposed to extreme conditions.
- Thermal Conductivity: Titanium has excellent thermal conductivity, which is beneficial when lasers produce heat. It helps the titanium components of the device dissipate the generated heat more efficiently, maintaining the device’s stability and preventing overheating.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium is non-toxic and highly biocompatible, which makes it a preferred material for medical lasers, particularly those used in surgery or skin treatments. It doesn’t cause adverse reactions when in contact with body tissues, making it safe for direct use in medical procedures.
Applications of Titanium Laser Devices
Titanium laser devices have found a place in several industries due to their precision and performance. Here are a few areas where these advanced tools are making significant contributions:
1. Medical and Healthcare
Titanium laser devices are increasingly popular in medical fields due to their precision and biocompatibility. Laser surgeries for skin, eyes (such as LASIK), and dental procedures benefit from titanium’s lightweight, strong, and non-corrosive properties. The laser’s precision allows for minimal damage to surrounding tissues, leading to quicker recovery times and less pain for patients.
2. Manufacturing and Metalworking
In industries that involve metal cutting and engraving, titanium laser devices are used for precision tasks. These lasers can cut through thick materials with high efficiency and fine detail. Titanium’s ability to withstand high temperatures makes it an excellent material for creating parts that will be used in high-performance environments, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
3. Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on materials that are both strong and lightweight to reduce fuel consumption and improve overall performance. Titanium laser devices are often used for cutting, welding, and engraving titanium components used in aircraft and spacecraft, ensuring the parts are fabricated to the highest standards of precision.
4. Jewelry and Watchmaking
Jewelry designers and watchmakers use titanium laser devices for engraving intricate designs and logos onto metal surfaces. Titanium’s resistance to corrosion and its lightweight nature makes it a popular choice in luxury watchmaking and fine jewelry.
5. Research and Development
In research labs, titanium laser devices are employed in experiments that require extreme precision, such as in laser spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and optical measurements. Their durability and accuracy make them an essential tool in advancing scientific studies.
Advantages of Titanium Laser Devices
- Enhanced Precision: Titanium laser devices offer unmatched precision, which is especially critical in medical and industrial applications where even the smallest error can lead to undesirable results.
- Longer Lifespan: Due to titanium’s corrosion resistance and ability to withstand wear and tear, these lasers tend to have longer operational lifespans compared to those made from other materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
- Cost Efficiency: Although titanium laser devices may come with a higher upfront cost, their durability and efficiency contribute to cost savings in the long run. They often require less maintenance and are more reliable, making them a sound investment for businesses and healthcare institutions.
- Minimized Environmental Impact: Titanium is a highly recyclable material, which reduces the environmental footprint of producing titanium laser devices. Additionally, their long lifespan contributes to less waste and fewer discarded devices over time.