Woodworking has long been an essential trade, with its roots stretching back to ancient civilizations. From creating simple tools and furniture to intricate wood carvings, the craft of woodworking has evolved significantly over the centuries Edge Banding Machine. In the modern era, woodworking machinery plays a pivotal role in enhancing both the efficiency and precision of carpentry. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of woodworking machinery, their uses, and how they’ve transformed the industry.
The Role of Woodworking Machinery in Modern Carpentry
Woodworking machinery encompasses a wide variety of tools designed to aid in the shaping, cutting, finishing, and assembly of wood products. These machines have revolutionized carpentry by reducing manual labor, improving accuracy, and increasing production speed. The increased demand for precision and mass production of furniture, cabinetry, and construction materials in recent years has driven the development of increasingly advanced machinery.
Types of Woodworking Machinery
Woodworking machinery can be categorized into several key types, each with specific functions and applications. Below are some of the most commonly used machines in woodworking:
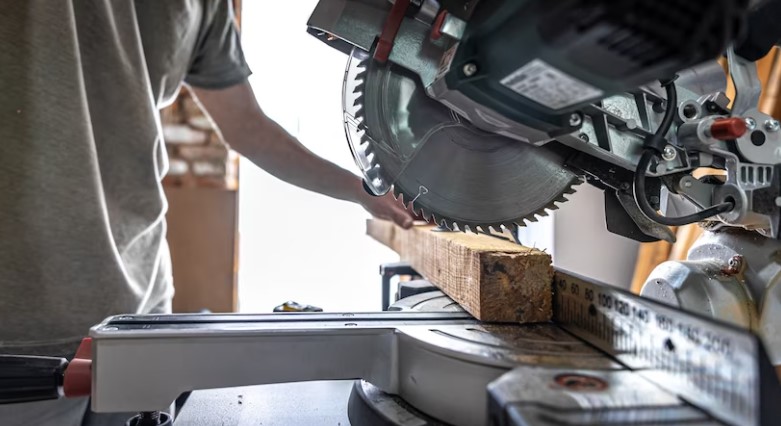
1. Table Saw
The table saw is one of the most essential pieces of machinery in a woodworking shop. It consists of a circular blade mounted on an arbor that extends through a flat table. The primary function of the table saw is to make straight cuts in wood, whether they are crosscuts (across the grain) or rip cuts (along the grain). A table saw is also capable of making bevel cuts, dado cuts, and even angled cuts, making it incredibly versatile for both professional carpenters and hobbyists.
2. Router
A router is a versatile tool used for hollowing out or shaping wood. It can be used to make grooves, decorative edges, and intricate designs in wooden surfaces. Routers come in various sizes, from handheld versions to larger, stationary models mounted on a router table. Some routers can also be equipped with specialized bits to create specific profiles and finishes.
3. Band Saw
A band saw features a long, continuous band of teeth that move over two wheels. It is primarily used for cutting curves and irregular shapes in wood, but it can also make straight cuts, especially for resawing thicker pieces of wood into thinner sheets. Band saws are essential in woodworking for both fine, detailed work and larger cuts.
4. Planer
A planer is used to smooth the surface of wood and adjust its thickness. It removes small amounts of material from the wood’s surface to create an even thickness across the entire board. This tool is invaluable when working with rough-sawn lumber that requires refinement or when multiple pieces need to be made to the same thickness for uniformity in projects.
5. Joiner
A joiner is a machine used to create flat edges on wood so that they can be joined together perfectly. It helps ensure that the edges are straight and square, which is essential for achieving strong, tight joints in cabinetry, furniture making, and woodworking in general.
6. CNC Router
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) routers are high-precision machines that are controlled by computer programs to perform intricate cutting and engraving tasks. These machines can handle complex designs and are used to produce highly detailed woodwork, from furniture components to decorative elements. The ability to automate precise cuts reduces human error and allows for mass production without compromising quality.
7. Drill Press
The drill press is a stationary machine used to bore holes in wood with precision. Unlike a handheld drill, the drill press provides a fixed and controlled drilling motion, allowing for more accurate and consistent hole placement. It can be used for drilling, sanding, and even mortising, depending on the attachment used.
8. Sanders
Sanders are used to smooth and finish wood surfaces by removing small amounts of material. There are various types of sanders, including belt sanders, orbital sanders, and drum sanders, each suited for specific tasks. Sanders ensure a smooth, even finish on wooden surfaces, which is especially important in the final stages of woodworking.
Benefits of Woodworking Machinery
The introduction and widespread use of woodworking machinery have led to several significant benefits in the industry:
1. Increased Efficiency
Woodworking machines allow tasks that once took hours to be completed in a fraction of the time. For example, machines like the table saw, planer, and CNC router can make multiple cuts and adjustments quickly, significantly improving overall workflow and productivity.
2. Improved Precision
With the aid of woodworking machinery, woodworkers can achieve an unprecedented level of precision. Machines like the CNC router, drill press, and joiner allow for consistent, accurate cuts and finishes that would be difficult, if not impossible, to replicate by hand.
3. Higher Production Capacity
Machines can work continuously and produce large volumes of workpieces, making them indispensable for mass production. This is particularly important in industries such as furniture manufacturing, where large quantities of products need to be produced in a relatively short amount of time.
4. Enhanced Safety
While woodworking can be hazardous, modern machines come equipped with advanced safety features, such as blade guards, automatic shut-off mechanisms, and safety switches. These features help minimize the risks associated with cutting and shaping wood, providing a safer working environment for carpenters.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial investment in woodworking machinery can be high, the long-term savings in time and labor can outweigh the cost. In addition, the consistency and precision of machine-made workpieces reduce material waste, contributing to a more cost-effective operation.
The Future of Woodworking Machinery
As technology continues to advance, the future of woodworking machinery looks bright. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into woodworking machines could lead to even more sophisticated machines that can adjust their operations in real-time based on materials, design specifications, and user preferences. Additionally, innovations in robotics and automation may further reduce the need for manual labor in woodworking shops.